Tutorials
These six tutorials targeted at future participants in the MANRS for Network Operators Program provide an introduction to MANRS, including the four Actions all network operators should implement to improve both the Internet’s routing security and their own network’s operational efficiency.
Who Should Take These Tutorials?
The target audiences are network administrators, network engineers, and other parties with a working knowledge of routing and security who are looking for steps to improve their network’s routing security.
About the Tutorials
Module 1: Introduction to MANRS

What is MANRS, and why should you join? MANRS is a global initiative to implement crucial fixes needed to eliminate the most common routing threats. In this module you will learn about vulnerabilities of the Internet routing system and how four simple steps, called MANRS Actions, can help dramatically improve Internet security and reliability.
Module 2: IRRs, RPKI, and PeeringDB
This module helps you understand the databases and repositories MANRS participants should use to document routing policy and maintain contact information. You’ll learn what database objects to use to document routing information related to your network and how to register information in the RPKI system. Finally, you will learn how to use the PeeringDB and other databases to publish your contact information.
Module 3: Global Validation: Facilitating validation of routing information on a global scale

This module helps you understand how to enable others to validate route announcements originating from your network by documenting a Network Routing Policy. You’ll learn what a Network Routing Policy is, how to document your organization’s Network Routing Policy and make it publicly available in order to signal to other networks which announcements from your network are correct.
Module 4: Filtering: Preventing propagation of incorrect routing information

In this module, you will learn how to prevent incorrect routing announcements from your customers and your own network. The module explains how filters can be built, including the tools used to build them. It also shows how to signal to other networks which announcements from the network are correct.
Module 5: Anti-Spoofing: Preventing traffic with spoofed source IP addresses
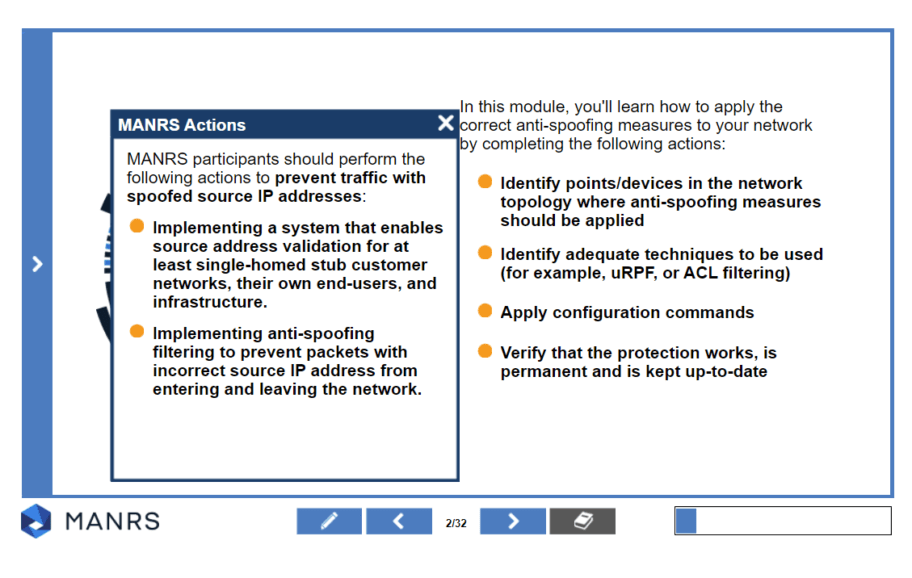
This module will help you apply anti-spoofing measures within your network. After this module you will be able to identify points/devices in the network topology where anti-spoofing measures should be applied, identify adequate techniques to be used (for example, uRPF, or ACL filtering), configure your devices to prevent IP spoofing, and verify that the protection works.
Module 6: Coordination: Global communication between network operators

This module is to understand how to create and maintain contact information in publicly accessible places. It explains why it is important to publish and maintain contact information, how to publish contact information to Regional Internet Registries (RIRs), Internet Routing Registries (IRRs), and PeeringDB, and what contact information you should publish to a company website.